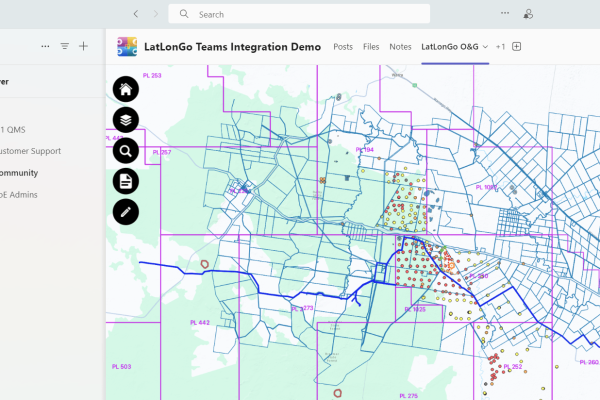
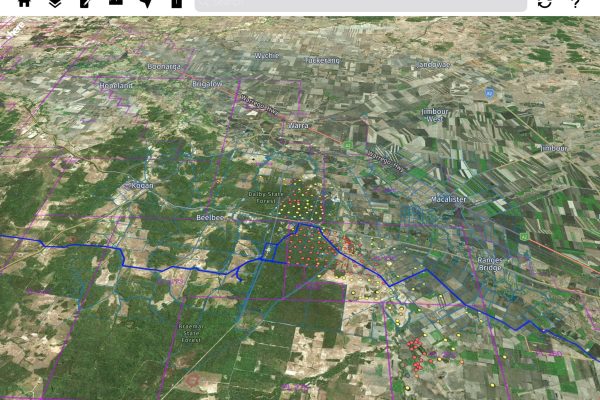
Maintaining a GIS is essential for ensuring its reliability and effectiveness. Regular system maintenance encompasses data updates, quality control processes, software patches, and hardware optimizations that collectively preserve spatial information accuracy and system performance. Without proper maintenance, organizations risk degraded analysis capabilities, visualization errors, and potentially flawed decision-making based on outdated or corrupted geospatial data.
A well-maintained GIS infrastructure not only extends the lifespan of technology investments but also enhances user adoption through consistent performance, ultimately maximizing the strategic value of location intelligence across departments and supporting time-sensitive operational requirements that depend on spatial insights.