Imagery/LIDAR technology has emerged as a transformative force in transportation, particularly in autonomous vehicles and infrastructure monitoring. This analysis examines the key costs and benefits associated with LIDAR implementation across various transportation sectors.
LIDAR operates by emitting laser pulses and measuring their return time to create detailed 3D maps of surroundings. Modern LIDAR systems can capture millions of points per second, offering unprecedented environmental awareness for vehicles and infrastructure monitoring systems.
1. Hardware Expenses
2. Integration Costs
3. Operational Costs
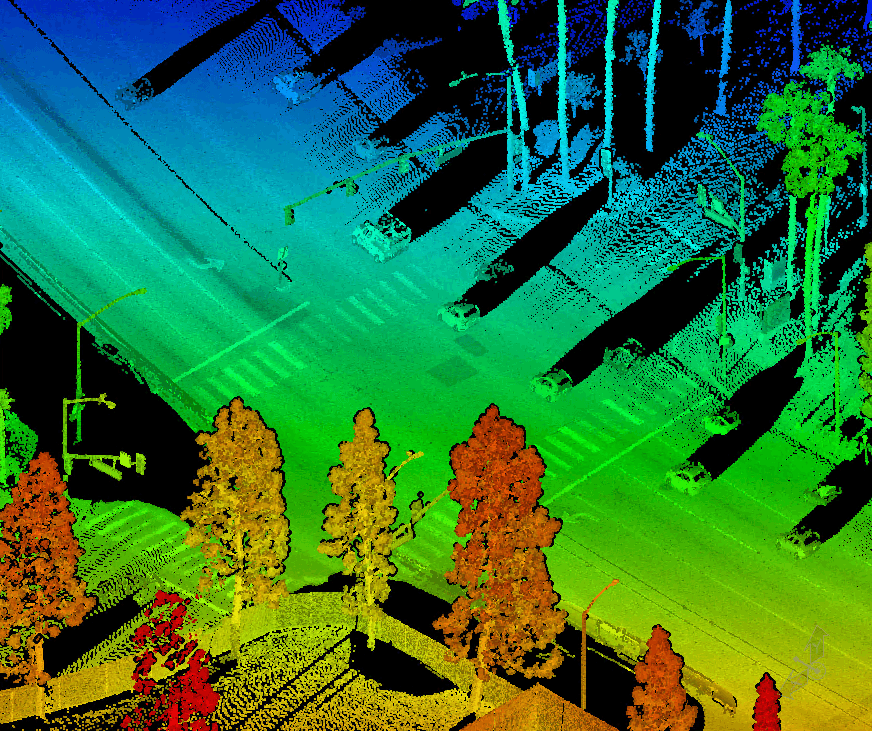
1. Safety Improvements
2. Operational Efficiency
3. Infrastructure Management
1. Enhanced Safety Features
2. Operational Advantages
3. Long-term Infrastructure Benefits
Requirements
1. Phased deployment approach
2. Risk Mitigation
3. Performance Monitoring

LIDAR technology represents a significant investment in transportation infrastructure but offers substantial returns through improved safety, efficiency, and operational capabilities. The initial costs are offset by long-term benefits, particularly in safety improvements and operational efficiency. Organizations should consider a phased implementation approach to maximize returns while minimizing disruption.